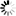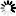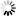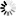By default, a new container starts operating in the host-routed mode. In this mode, the container uses a special network adapter, venet0, to communicate with the server where it resides, with the other containers on the server, and with computers on external networks. The figure below demonstrates an example network configuration where all containers are set to work in the host-routed mode.
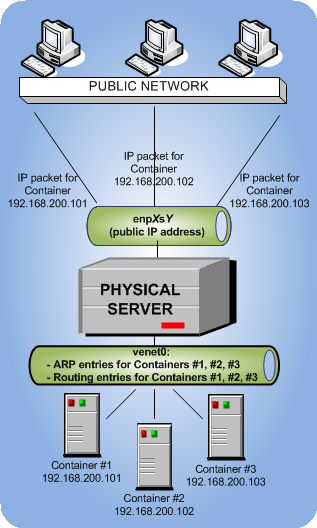
In this configuration:
-
Containers #1, #2, and #3 use the
venet0adapter as the default gateway to send and receive data to/from other networks. They also use this adapter to exchange the traffic between themselves. -
When containers #1, #2, and #3 start, the server creates ARP and routing entries for them in its ARP and routing tables. You can view the current ARP and routing entries on a server using the
arp -nandroute -ncommands. For example:# arp -n Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface 10.30.0.4 ether 00:1a:e2:c7:17:c1 C enp0s5 10.30.23.162 ether 70:71:bc:42:f6:a0 C enp0s5 192.168.200.101 * * MP enp0s5 192.168.200.102 * * MP enp0s5 192.168.200.103 * * MP enp0s5 # route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 192.168.200.101 * 255.255.255.255 UH 1000 0 0 venet0 192.168.200.102 * 255.255.255.255 UH 1000 0 0 venet0 192.168.200.103 * 255.255.255.255 UH 1000 0 0 venet0 10.30.0.0 * 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 enp0s5 default virtuozzo.com 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 enp0s5
As you can see, the ARP and routing tables contain entries about IP addresses 192.168.200.101, 192.168.200.102, and 192.168.200.103 that belong to containers 1, #2, and 3.
-
All container outgoing network traffic goes to the
venet0adapter and is forwarded via theenp0s5physical adapter to the destination, according to the routing table of the server. -
All container incoming network traffic is also processed by the
venet0adapter. Consider the following situation:- Computer X on the local network wants to send a data packet to container #1 with IP address 192.168.200.101, so it issues an ARP request which computer has this IP address.
- The server hosting container #1 replies with its MAC address.
- Computer X sends the data packet to the indicated MAC address.
-
The server receives the packet and transmits it to
venet0that forwards the packet to container #1.